Effector Process In Software Engineering 4,0/5 7336reviews

Main articles: and Legal requirements for the licensing or certification of professional software engineers vary around the world. In the UK, there is no licensing or legal requirement to assume or use the job title Software Engineer. In some areas of Canada, such as Alberta, British Columbia, Ontario, and Quebec, software engineers can hold the Professional Engineer (P.Eng) designation and/or the Information Systems Professional (I.S.P.) designation.
In Canada, there is a legal requirement to have P.Eng when one wants to use the title 'engineer' or practice 'software engineering'. In Europe, Software Engineers can obtain the (EUR ING) professional title. The United States, since 2013, has offered an exam for Software Engineering, thereby allowing Software Engineers to be licensed and recognized. Mandatory licensing is currently still largely debated, and perceived as controversial. In some parts of the US such as Texas, the use of the term is regulated by law and reserved only for use by individuals who have a license.
The and the, the two main US-based professional organizations of software engineering, publish guides to the profession of software engineering. The IEEE's Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge - 2004 Version, or, defines the field and describes the knowledge the IEEE expects a practicing software engineer to have. The most current SWEBOK v3 is an updated version and was released in 2014. The IEEE also promulgates a 'Software Engineering Code of Ethics'. Employment [ ] In November 2004, the counted 760,840 software engineers holding jobs in the; in the same time period there were some 1.4 million practitioners employed in the U.S. In all other engineering disciplines combined. Due to its relative newness as a field of study, formal education in software engineering is often taught as part of a computer science curriculum, and many software engineers hold computer science degrees and have no engineering background whatsoever.
Many software engineers work as employees or contractors. Software engineers work with businesses, government agencies (civilian or military), and non-profit organizations. Some software engineers work for themselves as. Some organizations have specialists to perform each of the tasks in the. Other organizations require software engineers to do many or all of them.
In large projects, people may specialize in only one role. In small projects, people may fill several or all roles at the same time. Specializations include: in industry (,,,,,, ) and in academia (, ). Most software engineers and programmers work 40 hours a week, but about 15 percent of software engineers and 11 percent of programmers worked more than 50 hours a week in 2008. Injuries in these occupations are rare.
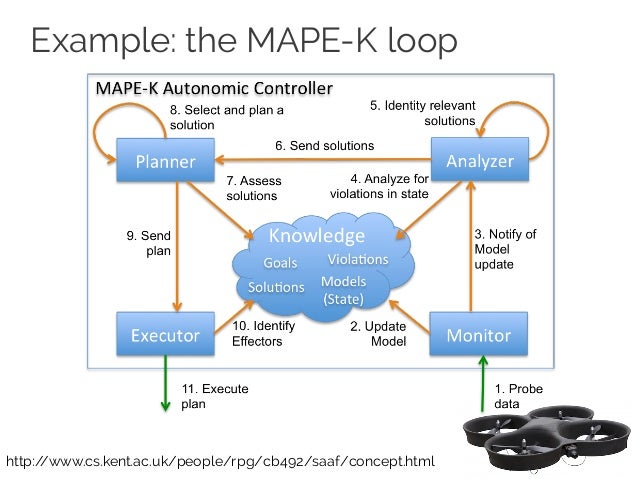
Software Engineering Assignment Help, Effector process, Question: Describe the effector process? Answer: The effector process is a procedure that verifies itself.
However, like other workers who spend long periods in front of a computer terminal typing at a keyboard, engineers and programmers are susceptible to eyestrain, back discomfort, and hand and wrist problems such as. The field's future looks bright according to and, which rated Software Engineer as the best job in the United States in 2006. In 2012, software engineering was again ranked as the best job in the United States, this time by CareerCast.com. Certification [ ] The offers certifications on specific topics like, process improvement and.,, and other companies also sponsor their own certification examinations. Many programs are oriented toward specific technologies, and managed by the vendors of these technologies.
These certification programs are tailored to the institutions that would employ people who use these technologies. Broader certification of general software engineering skills is available through various professional societies. As of 2006, the had certified over 575 software professionals as a (CSDP). In 2008 they added an entry-level certification known as the Certified Software Development Associate (CSDA). The had a professional certification program in the early 1980s, [ ] which was discontinued due to lack of interest. The ACM examined the possibility of professional certification of software engineers in the late 1990s, but eventually decided that such certification was inappropriate for the professional industrial practice of software engineering. The has developed a legally recognized professional certification called Chartered IT Professional (CITP), available to fully qualified members ( MBCS).
Software engineers may be eligible for membership of the and so qualify for Chartered Engineer status. In Canada the has developed a legally recognized professional certification called Information Systems Professional (ISP). In Ontario, Canada, Software Engineers who graduate from a Canadian Engineering Accreditation Board (CEAB) accredited program, successfully complete PEO's ( Professional Engineers Ontario) Professional Practice Examination (PPE) and have at least 48 months of acceptable engineering experience are eligible to be licensed through the Professional Engineers Ontario and can become Professional Engineers P.Eng. The PEO does not recognize any online or distance education however; and does not consider Computer Science programs to be equivalent to software engineering programs despite the tremendous overlap between the two.
Opmanager 11 Keygen Mac. This has sparked controversy and a certification war. It has also held the number of P.Eng holders for the profession exceptionally low.
The vast majority of working professionals in the field hold a degree in CS, not SE. Given the difficult certification path for holders of non-SE degrees, most never bother to pursue the license. Impact of globalization [ ] The initial impact of outsourcing, and the relatively lower cost of international human resources in developing third world countries led to a massive migration of software development activities from corporations in North America and Europe to India and later: China, Russia, and other developing countries. This approach had some flaws, mainly the distance / timezone difference that prevented human interaction between clients and developers and the massive job transfer. This had a negative impact on many aspects of the software engineering profession.
For example, some students in the avoid education related to software engineering because of the fear of (importing software products or services from other countries) and of being displaced. Although statistics do not currently show a threat to software engineering itself; a related career, does appear to have been affected.
Nevertheless, the ability to smartly leverage offshore and near-shore resources via the workflow has improved the overall operational capability of many organizations. When North Americans are leaving work, Asians are just arriving to work. When Asians are leaving work, Europeans are arriving to work.
This provides a continuous ability to have human oversight on business-critical processes 24 hours per day, without paying overtime compensation or disrupting a key human resource, sleep patterns. While global outsourcing has several advantages, global - and generally distributed - development can run into serious difficulties resulting from the distance between developers. This is due to the key elements of this type of distance that have been identified as geographical, temporal, cultural and communication (that includes the use of different languages and dialects of English in different locations). Research has been carried out in the area of global software development over the last 15 years and an extensive body of relevant work published that highlights the benefits and problems associated with the complex activity. As with other aspects of software engineering research is ongoing in this and related areas. Related fields [ ] Software engineering is a direct sub-field of and has an overlap with and [ ]. It is also considered a part of overall.
Computer Science [ ]. This section needs expansion. You can help. (July 2017) In general, software engineering focuses more on techniques for the application of software development in industry, while computer science focuses more on algorithms and theory. Controversy [ ] Over definition [ ] Typical formal definitions of software engineering are: • 'the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of '. • ^, pp. 1–1 • ACM (2007)..
Retrieved 2010-11-23. • Laplante, Phillip (2007).. Boca Raton: CRC.. Retrieved 2011-01-21. • Systems and software engineering - Vocabulary, // std (E), 2010. • ^ IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology, std 6, 1990. • ^ (2007) [1982].
'1.1.2 What is software engineering?' Harlow, England: Pearson Education. Software engineering is an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production from the early stages of system specification to maintaining the system after it has gone into use. In this definition, there are two key phrases: 1.
Engineering discipline Engineers make things work. They apply theories, methods and tools where these are appropriate [...] Engineers also recognize that they must work to organizational and financial constraints.
All aspects of software production Software engineering is not just concerned with the technical processes of software development but also with activities such as software project management and with the development of tools, methods and theories to support software production. • ^ 'Software Engineering'.
Information Processing. North-Holland Publishing Co.year = 1972. • Leondes (2002). Intelligent systems: technology and applications. 1.4 Computers and a First Glimpse at Al (1940s) • Campbell-Kelly, Martin (April 1982). 'The Development of Computer Programming in Britain (1945 to 1955)'.
IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 4 (2): 121–139.. • (March 1968). 11 (3): 147–148.:.
Retrieved 2009-08-10. • (December 1972)... 15 (12): 1053–1058.:. Retrieved 2008-12-26. Retrieved 17 Nov 2017. • Randall, Brian..
Retrieved 17 Nov 2017. • Selby, Richard. Software Engineering: Barry W. Boehm's Lifetime Contributions to Software Development, Management, and Research.. • Tedre, Matti (2014).
Science of Computing: Shaping a Discipline. •, p. 26 • Peter, Naur; (7–11 October 1968).
Garmisch, Germany: Scientific Affairs Division, NATO. Retrieved 2008-12-26. • (10 August 2001).. Brian Randell's University Homepage. The School of the Computer Sciences, Newcastle University. Retrieved 2008-10-11. The idea for the first NATO Software Engineering Conference, and in particular that of adopting the then practically unknown term 'software engineering' as its (deliberately provocative) title, I believe came originally from Professor.
• Boehm (1981). Software Engineering Economics. • Humphrey, Watts S. Managing the Software Process.
Retrieved 2012-04-01. IEEE Computer Society.
Retrieved 24 May 2016. • Abran, Alain, ed. (2005) [2004]... Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society.. Retrieved 2010-09-13. The total volume of cited literature is intended to be suitable for mastery through the completion of an undergraduate education plus four years of experience.
Retrieved 2012-03-25. • Degree programs in Software Engineering • Williams, N.S.W.
(19–21 February 2001). 'Professional Engineers Ontario's approach to licensing software engineering practitioners'. Software Engineering Education and Training, 2001 Proceedings. 14th Conference on. Charlotte, NC:. Retrieved 2012-04-01. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
Retrieved 2012-03-25. • Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor,, Table 1. Retrieved 2008-02-01. Retrieved 2009-12-17.
• Kalwarski, Tara; Daphne Mosher; Janet Paskin; Donna Rosato (2006).. MONEY Magazine. Retrieved 2006-04-20. Retrieved 2017-11-03. Retrieved 2012-03-25. • Wyrostek, Warren (March 14, 2008).. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
• IEEE Computer Society. Retrieved 2007-04-10. Retrieved 2010-04-20.
• ACM (July 17, 2000). Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). Archived from (PDF) on May 17, 2008. Retrieved 2009-03-03. At its meeting in May 2000, the Council further concluded that the framework of a licensed professional engineer, originally developed for civil engineers, does not match the professional industrial practice of software engineering. Such licensing practices would give false assurances of competence even if the body of knowledge were mature; and would preclude many of the most qualified software engineers from becoming licensed. • Canadian Information Processing Society..
Retrieved 2007-03-15. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
• Thibodaux, Patrick (2006-05-05).. Retrieved 2016-12-06.
Retrieved 2012-03-25. • Mullins, Robert (2007-03-13).. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
Retrieved 2012-03-25. • Casey, Valentine (2010-08-20).. Retrieved 2013-12-06. • • • • Akram I.
Salah (2002-04-05). 35th Annual Midwest Instruction and Computing Symposium. Retrieved 2006-09-13.: 'For some, software engineering is just a glorified name for programming. If you are a programmer, you might put 'software engineer' on your business card—never 'programmer' though.' • Mills, Harlan D., J. Newman, and C.
Engle, Jr., 'An Undergraduate Curriculum in Software Engineering,' in Deimel, Lionel E. Software Engineering Education: SEI Conference 1990, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, April 2–3. Springer..,: 'As a practical matter, we regard software engineering as the necessary preparation for the practicing, software development and maintenance professional. The Computer Scientist is preparing for further theoretical studies.' • David Budgen; Pearl Brereton; Barbara Kitchenham; Stephen Linkman (2004-12-14).. Retrieved 2006-10-18.: 'We believe that software engineering can only advance as an engineering discipline by moving away from its current dependence upon advocacy and analysis.'
Agile Alliance. Minecraft Mega 3d Resource Pack Download. Retrieved 14 June 2010. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
References [ ] • Abran, Alain; Moore, James W.; Bourque, Pierre; Dupuis, Robert; Tripp, Leonard L. Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge. • Sommerville, Ian (2008). Pearson Education.. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
Further reading [ ] • (2009). Software Engineering: A Practitioner's Approach (7th ed.). Boston, Mass: McGraw-Hill.. • (2010) [2010]. Harlow, England: Pearson Education..
• (2005) [1991]. •; Dutoit, Allen (2009). Object-oriented software engineering: using UML, patterns, and Java (3rd ed.).
Prentice Hall.. External links [ ] Wikimedia Commons has media related to.
Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Wikiversity has learning resources about • • OpenSDLC.org the integrated Creative Commons SDLC • Carnegie Mellon • Software Engineering Society.

